KTU is integrating the United Nations sustainable development goals (17 SDG) in all areas of its activity. The University aims to develop responsible future leaders and specialists in their areas, and attempts to achieve long-term goals concerning well-being of people and environment. Following the guidelines of socially responsible activities, the University conducts educational activities, initiates projects; the principles of sustainable development are integrated in various University’s activities.
According to this attitude, the University aims for new knowledge and technologies to serve for the well-being of the people and the environment. It includes focusing on cultivating the culture of sustainable development and responsibility within the University’s community and strengthening of the University’s responsibility to the environment, society and region.
KTU’s strategy is aimed at strengthening the University’s responsibility to society and the country by consolidating its activities to improve the quality of human life and accelerate the development of statehood. Responsible attitude towards environment and the society at the University is based on the philosophy of sustainable development activities, such as:
KTU acts in a responsible manner based on the common university values: Responsibility to society; Cooperation; Continuous improvement.
Coordinates activities
Internal Communication Department
Tel. +370 608 21 745
Email sustainability@ktu.lt
Composition of the working group on the implementation of the Sustainable Development Guidelines:
The Guidelines for Emotional and Social Welfare Policy and Implementation Thereof at Kaunas University of Technology (hereinafter – Guidelines) set out the application of the principles of emotional and social welfare and implementing measures thereof at the University by identifying the target groups of community members and the responsibilities of the persons involved in this process.
In order to fully implement the principles of the European Charter for Researchers and the Magna Charta of the European Universities, Kaunas University of Technology organises its activities while creating an open environment where individual differences, characteristics, potential and contribution of all its staff and students are acknowledged and appreciated. Each employee and student has a right to work and study in the environment that encourages respect to everyone’s dignity.
To foster and ensure the implementation of the fundamental human rights which are set out in the Constitution of the Republic of Lithuania and the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union, the Equality and Diversity Policy was approved and the University’s Equality and Violence Prevention Committee was established.
The members of the University’s Equality and Violence Prevention Committee:
Tasks of the Equality and Violence Prevention Committeee:
The Committee operates as an independent, objective and impartial body without any preconceived notions regarding discrimination, harassment, sexual harassment, violations of equal opportunities and cases of violence and the perpetrators of alleged violations.
KTU aims to be an open, tolerant, leading university in Lithuania, an attractive employer that creates an inclusive, emotional, and physically health-friendly work environment and culture, in which the individual differences, personal qualities, professional competencies, and contribution to the development of the university’s activities are recognized and valued. KTU implements the project “Updating the Gender Equality Plan of the Kaunas University of Technology and integration into the organizational culture through the model of general competencies”, no. 10-040-T-003, financed by the funds of the European Union for the years 2021-2027, the measures for economic revitalization and increasing resilience of “New Generation Lithuania” and the state of the Republic of Lithuania. The project will update and expand KTU’s gender equality plan, paying special attention to issues of violence and harassment prevention and other forms of inequality (race, nationality, language, origin, social status of refugees, faith, beliefs or views, age, disability, sexual orientation, ethnicity, religion or other features of inequality) for elimination. Also, KTU’s model of general competencies will be updated with competencies that are necessary for the implementation of the new gender equality plan, on the basis of which training will be prepared for the academic and non-academic communities of the university. You can also read about the project here (information in Lithuanian).
Possible cases of violation of equal opportunities or misconduct may be reported to the University by email or in the electronic system of KTU employee:
* – access is possible through a secure connection via a virtual private network only.
KTU sustainable development related activities are implemented according to the programmes of the United Nations:
10 UN Global Compact Principles UN Global Compact (Principles)
Global Compact is the largest voluntary social responsibility initiative of companies/corporations that has two main goals:
1) To help companies introduce the principles of Global Compact in their business strategy
2) To promote cooperation and partnership between various sectors within and outside the state to achieve the universal goals of global development
Global Compact is based on the principles of human rights, labour force and environmental protection that are established in the following international documents:
2015 September. The United Nations General Assembly has announced 17 global sustainable development goals, 169 targets and 230 indicators to meet by 2030.
The goals of sustainable development are a strategic direction for the development of the world, focused on various actors, taking bold and change-promoting measures.
The point is to take immediate action to “steer the world in a sustainable and flexible direction” “without leaving anyone aside”, as implementation is based on “fully beneficial cooperation between present and future generations”.
5 key elements for action on sustainable development goals:
At the heart of the concept of sustainable development is the constructive interaction of the three main components – the environment, the economy and society.
For the generation that can be named as:
Human rights
Principle 1. Businesses should support and respect the protection of internationally proclaimed human rights.
Principle 2. Make sure that they are not complicit in human rights abuses.
Labour force
Principle 3. Businesses should uphold the freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining.
Principle 4. Elimination of all forms of forced and compulsory labour.
Principle 5. Abolition of child labour.
Principle 6. Elimination of discrimination in respect of employment and occupation.
Environment
Principle 7. Businesses should support a precautionary approach to environmental challenges.
Principle 8. Undertake initiatives to promote greater environmental responsibility.
Principle 9. Encourage the development and diffusion of environmentally friendly technologies.
Anti-corruption
Principle 10. Businesses should work against corruption in all its forms, including extortion and bribery.

KTU ‘s Objectives to Achieve Goal # 1
1.1. Meeting basic needs is a prerequisite for greater public involvement in sustainable development. Therefore, the relevant faculties or research groups of KTU can significantly contribute to the reduction of poverty and economic exclusion in Lithuania, Europe or other countries of the world.
1.2. Integration of social (poverty) themes in interdisciplinary research.
1.3. Quality education – to avoid poverty.
1.4. KTU graduates are job creators.
1.5. KTU’s contribution to the improvement of the national social security system and measures.
1.b. to carry out research and analysis identifying the impact of investments on the reduction of poverty and social exclusion in Lithuania

KTU Objectives to Achieve Goal # 2
2.2. KTU to develop and promote proper eating habits and abilities
2.4. Research and implementation of a sustainable food production, supply and consumption system

KTU Objectives # 3 to achieve
3.4. Services and training for the KTU community on non-communicable diseases and promotion of mental health and well-being
3.5. Strengthen the prevention and treatment of substance abuse (narcotic drugs and alcohol)
3.6. Integrating road safety and responsible driving into a sustainable mobility plan to reduce traffic risks
3.9. Pollution prevention and management by reducing the impact on human health.
3.9. Indoor and outdoor air quality research for safe work and studies at KTU
3.a. Implement tobacco prevention measures and initiatives

KTU Objectives to Achieve Goal # 4
4.3. Equal opportunities for men and women to study
4.4. Integrate entrepreneurial competencies for students in order to achieve higher employment of graduates and their contribution to the growth of public welfare
4.5. To provide opportunities for people with disabilities to study and work at KTU on an equal footing
4.7. Until 2030 to ensure that ALL learners acquire the knowledge and skills needed to promote sustainable development, including, but not limited to, education for sustainable development and the promotion of sustainable living, human rights, gender equality, peace and non-violent culture, global citizenship and cultural diversity and the contribution of cultures to sustainable development; development evaluation issues
4.a. Ensure a safe, non-violent, inclusive and effective learning environment at KTU
4.b. Integrate (for scholarships, invite students to study) students from developing countries into globally relevant study and research programs

KTU Objectives to Achieve Goal # 5
5.1. Discrimination against women at KTU is intolerable
5.2. Tolerance of all forms of violence against women and girls
5.2. KTU Research and Recommendations for Avoiding Violence
5.4. Promoting shared responsibility (men and women) in the household and in the family
5.5. Full and effective participation of women and equal opportunities for leadership at all levels of decision-making
5b. The use of enabling technologies, especially ICT, to promote women’s rights is research into the potential of innovative technologies
5.c. Gender equality issues are integrated into KTU’s policy, strategy and all regulations and procedures

KTU Objectives # 6 to achieve
6.3. Improving water quality: (a) wastewater treatment technologies and systems; (b) responsible waste management (increasing recycling and safe re-use and eliminating landfills); (c) reducing the potential for other pollutants to enter water bodies
6.3. Promoting the responsible use of inland waters (sustainable tourism, responsible behavior)
6.4. Improving water efficiency: a) equipment and technology; (b) information; (c) awareness; (d) innovation
6.a. International and sectoral cooperation and research on water quality and efficiency management
6.b. Promoting local community initiatives, capacity building and involvement in water quality and resource management

KTU Objectives to Achieve Goal # 7
Information is being prepared.

KTU Objectives to Achieve Goal # 8
Information is being prepared.

KTU Objectives to Achieve Goal # 9
Information is being prepared.

KTU Objectives to Achieve Goal # 10
Information is being prepared.

KTU Objectives to Achieve Goal # 11
Information is being prepared.

KTU Objectives to Achieve Goal # 12
Information is being prepared.

KTU Objectives to Achieve Goal # 13
Information is being prepared.

KTU Objectives to Achieve Goal # 14
Information is being prepared.

KTU Objectives to Achieve Goal # 15
Information is being prepared.

KTU Objectives to Achieve Goal # 16
Information is being prepared.

KTU Objectives # 17 to achieve the goal
17.7. Encourage the development, transfer, dissemination and dissemination of environmentally sound technologies in cooperation with business, governmental and international organizations
17.8. Contribute to the application and development of enabling technologies, in particular information and communication technologies.
17.9. To contribute to the strengthening of effective and targeted capacities for the KTU community, the society of Kaunas and the whole of Lithuania, helping to achieve the goals of sustainable development
17.14. Ensure policy coherence for sustainable development at KTU
17.16. Expand the partnership for sustainable development, complemented by multi-stakeholder partnerships that bring together and share knowledge, expertise, technology and financial resources to support the achievement of sustainable development goals and their understanding of their importance in society
5/17/17 KTU to cooperate with organizations and associations that carry out or coordinate activities for sustainable development. KTU to play a proactive role in implementing sustainable development measures not only at KTU but also at the city or national level.
17.19. Follow existing initiatives to develop indicators for measuring progress in sustainable development to monitor KTU’s sustainable development activities and to prepare and publish sustainable development reports. Periodically review and improve the sustainable development strategy and plans, updating and complementing them with appropriate measures
One of the main goals of sustainable development, to which the University responds, is Quality Education (# 4).
Through studies, research and the management of the University’s infrastructure, we directly contribute to the fostering of a culture of sustainable development and form a responsible approach of the University to solutions relevant to society, business, the region and the environment.
Therefore, purposeful partnership (# 17) with business, social and other scientific and non-governmental organizations has a direct impact and creates value for the Kaunas and Lithuanian region, and international partnerships lead to the implementation of regional or global challenges.
The University supports the development of sustainable and smart cities (# 11). Together with the public sector and business, it contributes to the development of smart cities and a more sustainable environment to make the daily lives of people and businesses in the city as comfortable as possible.
The University develops resilient infrastructure, promotes inclusive and sustainable industrialization and contributes to innovation (# 9). The University also ensures sustainable consumption and production patterns (# 12) and takes urgent action to combat climate change and its effects (# 13).
The University strives to ensure a healthy life and promotes the well-being of all age groups (# 3). Promotes sustainable, inclusive and sustainable economic growth, productive employment and decent work (# 8). Efforts are being made to achieve gender equality and empower women and girls (# 5).
The coordinating representative – Lolita Jurkšienė lolita.jurksiene@ktu.lt

The direct activities of the University do not contradict the values of sustainability implemented in the process of science and studies, they contribute to the establishment of these values and the demonstration of good examples.
KTU acts responsibly, based on the values of the university: The spirit and traditions of the University; responsibility to society; cooperation; transparency of activities; initiative; creativity; professionalism; academic integrity; continuous improvement.
The University adheres to international agreements and agreed principles of conduct, and also promotes social initiatives.
KTU voluntarily incorporates social and environmental principles into its activities.
The University works not only for the benefit of the KTU community, but also for the benefit of society as a whole.
The coordinating representative – Adriana Kviklienė adriana.kvikliene@ktu.lt
The University carries out educational activities, initiates projects, and integrates the principles of sustainable development in various activities of the University.
The university invests in human capital.

The aim is for new knowledge and technology to serve not only human well-being but also the environment. A culture of sustainable development and responsibility in the University community is purposefully fostered, contributing to ensuring the sustainability of KTU and strengthening responsibility for the environment, society and the region.
Research and results integrate sustainable development goals, which make a direct contribution to regional and KTU coherence.
Affordable and clean energy (# 7)
University participates in the development of modern renewable energy systems (# 7)
2019 The roof of the building complex of the IX building of Kaunas University of Technology was covered with solar energy elements, a solar power system was installed, integrating solar energy, its storage and coordination of flows. The total area is 5.5 thousand. sq.m. meters. It holds 1520 photovoltaic solar modules. The unique project has won worldwide recognition at the Energy Globe Awards.
The University is determined to continue implementing and developing alternative energy solutions.
The solar cell created by KTU Faculty of Chemical Technology V. Getautis together with other scientists is as much as 29.15 percent. the falling light converts it into electricity. This is a global record for the efficiency of solar cells. Self-assembled organic semiconductors are inexpensive. They cover the electrode of the solar cell with a thin, only a few nanometers thick molecular layer, which consumes a very small amount of material. It is estimated that 1 g of this semiconductor can cover a surface area of 1000 m2. It is very important that the development of silicon-perovskite tandem solar cells utilizes the existing production capacity of silicon solar cells, so the business will not need significant additional investment.
The professor’s work with co-authors was published in the world’s most famous scientific journal, Science.
Good health and well-being (# 3)
University strives for a healthy life, participates in the development of smart health technologies (# 3)
Researchers at the KTU Institute for Biomedical Engineering have developed a smart bracelet that automatically recognizes atrial fibrillation (arrhythmia), a condition that can lead to serious complications and even death if not detected in time. More than 1 percent. all populations have this disorder. Due to a rapidly aging society, the scale of the disease is expected to increase to 3 times worldwide over the next 30 years.
The bracelet is a non-invasive, comfortable device that allows you to monitor a person’s condition. When the photoplethysmographic signal detects heart activity close to atrial fibrillation, the device vibrates gently – asking the patient to touch the device with the other hand. In this way, a short electrocardiographic signal is recorded for control signal analysis.
The smart bracelet is easy to use. It is designed for seniors, people who value smart devices and technology with extreme caution.
A team of researchers from the Institute for Biomedical Engineering is further developing the smart bracelet by introducing additional features such as cardiac response monitoring algorithms.
KTU Faculty of Informatics researcher prof. R. Maskeliūnas and his team developed a method based on deep learning, based on which the onset of Alzheimer’s disease can be predicted from brain images. The algorithm is more than 99 percent. separates images of the brain affected by the disease by analyzing the magnetic resonance imaging images of 138 subjects. The new method is more accurate than the previous ones. The new algorithm could also be used to develop software that would automatically analyze data collected from vulnerable groups (over 65 years of age, experienced brain injuries, high blood pressure, etc.) – the system would alert medical staff of anomalies associated with the onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
KTU Institute of Health Telematics Science prof. A. Ragauskas together with the team invented and patented a non-invasive method of measuring head pressure. High head pressure, which can be caused by a head injury or brain tumor, can be fatal. Across Europe, around 2.5 million people are affected by brain injuries each year. people, and 75 thousand. such cases result in death. Effective measures can be taken when an increase in head pressure is observed in a timely manner, but the current method of measuring head pressure is based on an invasive procedure – surgical implantation of sensors into the human brain. Invasion of the brain poses a risk to the patient, and this procedure is not possible in all circumstances. The invented device makes it possible to measure head pressure without invading the brain, which has not been possible until now. This allows doctors to start treatment in a timely manner that can save the patient’s life.
KTU prof. Researchers of K. Baršauskas Institute of Ultrasound together with LSMU researchers have developed a non-invasive method of diagnosing melanoma.
Removal of the primary tumor remains necessary in the diagnosis of melanoma, and the decision to operate is usually based on a dermatoscopic assessment of the lesion. The accuracy of skin melanoma diagnosis without surgery is only 65 percent. and is highly dependent on the experience of the dermatologist performing the test.
Based on the analysis of diagnostic images from 100 patient samples, a scientifically developed and patented automated diagnostic system can detect melanoma by more than 90 percent. accuracy. The novelty of the method and technology is based on the fact that the combined diagnostic information is obtained by non-invasive imaging technologies operating on different physical principles. The developed automated system can complement the non-invasive diagnostic methods already used in clinical practice by automatically reliably distinguishing melanoma from melanocytic moles. Effective diagnosis of early-stage malignancies would shorten the time required for the study, allowing more patients to be tested during the routine time of the study.
Based on the results of the research, a prototype of the technology was developed. studies are being continued in a clinical setting.
Researchers at the KTU Food Institute are developing innovative products for personalized nutrition with the participation of an interested group of consumers. Seniors were invited to the creative process. 18 seniors over the age of 65 participated in the project “Consumer Involvement Laboratory”. During the project, they used a variety of new product development methodologies, offering both innovative (protein sauces) and simple ideas (more shredded products, more expressive and informative packaging). The seniors who participated in the practical seminars had the opportunity to participate in joint activities with KTU researchers and not only to see how new products are being developed, but also to create products that meet the expectations of Lithuanian seniors themselves.
Clean water and hygiene (# 6)
University contributes to the implementation of the European Green Course (# 6)
Researchers at the Department of Environmental Technology, KTU Faculty of Chemical Technology, have introduced and are continuing to test a hybrid system of advanced oxidation and sorption with a biologically active adsorbent. It allows to achieve very high efficiency of contaminated water treatment.
Various organic pollutants – phthalates, pharmaceuticals, pesticides – are still found in the treated water of domestic wastewater treatment plants. Scientists around the world agree that these pollutants have a negative impact on aquatic ecosystems and can also enter the human body because the substances are found in drinking water and the food we eat.
The polluted water treatment process proposed by the researchers of KTU Department of Environmental Technology is carried out in 2 stages:
Microorganisms attached to the surface of the activated carbon form a biofilm and decompose contaminants in the water. During such a complex process, the time of using activated carbon in the system is significantly extended and a very high efficiency of contaminated water treatment is achieved.
Such a water treatment system can be easily adapted to treat both domestic and industrial wastewater contaminated with persistent organic pollutants. The introduction of this technology in various industrial and agricultural sectors and the re-use of treated water could significantly reduce the cost of clean water from nature.
Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure (# 9)
University promotes inclusive and sustainable industrialization and contributes to innovation (# 9)
KTU Faculty of Chemical Technology prof. J. V. Gražulevičius and his team develop, synthesize and research organic non-metallic radiators (non-metallic fluorescent substances), which replace inorganic-based devices that use precious and rare metals. Organic LEDs, unlike inorganic ones, can be flexible and large enough in area. Emitters have a highly efficient emission, with quantum yields of up to 100%. Using these radiators, the devices can be formed both by vacuum evaporation and by a much more technological, economical and environmentally friendly method of casting solutions. One of their main applications is organic light emitting diodes, which are used in industry for the production of televisions, computers, telephone screens and various lighting devices. These new materials are expected to lead to greener electronic devices with higher efficiencies, simpler device designs and lower production costs. KTU researchers work together with an international consortium of researchers from 8 countries around the world.
While evolving technologies are helping companies to better protect their products from counterfeiters, the growing number of counterfeits shows that this is not enough. The technologies and possibilities used to form holograms have changed over the past decades, but the principle of operation has remained the same: white light illuminates the space in light with diffractive gratings.
Together with a team of researchers from the Department of Multimedia Engineering, KTU Faculty of Informatics, the project “Development and Implementation of a Hologram Diffractive Image Projection Algorithm for Smart Devices (HoloApp)” was implemented. The project uses a femtosecond laser to develop a new technology for direct hologram recording on the surface and an intuitive user interface that generates hologram images for a smart Android platform device. It has been possible to display the colors of the hologram properly on the screen of the smart device, and the integrated gyroscope allows the shades of holograms and visible images to change as you would in a real hologram when you use the device in your hand. Using an advanced femtosecond laser, material is simply removed from the illuminated areas, forming the desired surface relief in the metal foil. Because holograms typically take time to produce, this solution allows potential customers to show what their product will look like without producing the test mark itself.
Hologram production is a sufficiently long process that requires complex equipment and specialized knowledge. Holograms are constantly introducing new technologies and materials, making it increasingly difficult to copy holograms.
Researchers at KTU Faculty of Electrical and Electronics have developed an innovative speedometer and system: the speed of a car is determined in less time and more accurately.
Speedometers are identified as an effective means of encouraging drivers not to exceed the speed limit. Rapid measurement of vehicle speeds is essential for more efficient traffic control, as well as rapid data processing and transmission without compromising information quality.
The system, developed by KTU researchers, is designed for traffic monitoring, vehicle classification, speed measurement and vehicle number plate identification at any time of the day in all weather conditions. The new calculation method is adapted to measure the average speed on a given road section using two meters at a certain distance from each other with the means of vehicle identification. If the speed of the vehicles is measured in order to simultaneously identify the vehicles exceeding the speed at that location, a method of their identification is also required. Using the invention of KTU scientists, a conventional method of vehicle identification can be used, where the vehicle registration number is recorded by video cameras. The video capture camera shall be positioned at such a distance from the speedometers that the speed measurement device shall be able to process the data for determining the speed of the vehicle and transmit a signal so that the video capture camera is ready to capture and capture the vehicle. Magnetic sensors that help determine the speed of vehicles must be located in the area of the video camera, in the middle of the traffic lane, below the surface of the carriageway. These sensors determine not only the speed of the vehicle, but also the value.
Sustainable Cities and Communities (# 11)
University contributes to inclusive and sustainable urbanization (# 11)
In 2020, G. Balčytis, Associate Professor and Architect of KTU Faculty of Construction and Architecture, won the National Culture and Art Prize for architecture open to the city and people. The architect has already been awarded the Badge of Honor of the Lithuanian Union of Architects and the Government Culture and Art Prize, and is almost best known as the author of the projects for the reconstruction of the Kaunas bus station and the exclusive Vilkaviškis bus station.
Many cities want to stand out with their architecture and be famous for their world-class buildings – landmarks. However, such objects are often built regardless of the specifics of the area, which greatly alters and sometimes erodes the long-established environment. According to G. Balčytis, architecture is the art of spaces, not planes. For this reason, it is especially important what space the building creates for itself, the street next door and, in general, what space the city creates.
The architect G. Balčytis, who designed the Kaunas bus station together with his colleagues, proved that the exceptional architectural expression of the building is a strong motive for the building to become a city sign, create a distinctive face for several decades of change and enjoy the quality of the urban environment.
“It is said that new buildings are no longer needed, but it is necessary to renovate or replace old buildings – so that they meet today’s requirements and are suitable for the future. If the building can be adapted to these times, it is both a great advantage and a challenge for architects, because the world has never changed so fast, ”says G. Balčytis.
University students gain the knowledge, skills and understanding to contribute to building a sustainable future.
Coordinating representative – Kristina Ukvalbergienė kristina.ukvalbergiene@ktu.lt

The quality, effectiveness and efficiency of the University’s activities are inextricably linked to responsible, environmentally friendly behaviour; therefore, the University integrates the principles of quality and sustainable development (#16) and develops a culture of quality and ecology (#15).
The University’s strategy is aimed at strengthening the University’s responsibility towards society and the country (#16) by consolidating its activities to improve the quality of human life and accelerate the development of statehood (#11). The most important activity in this direction is the shaping and transfer of the University’s contribution to the country’s vitality and its sustainable economic, socio-cultural, and knowledge-based development. The University’s objectives and activities are focused on people and their well-being (#1), both within and outside the University:
The Description of the Internal Study Quality Assurance System of the University lists the principles of responsible management that guide the University’s studies. Some of them are focused on sustainable development, social responsibility, equal opportunities and diversity and inclusion (6.1 Sustainable Development, 6.2 Inclusive Education, 6.4 Ensuring Equal Opportunities and Diversity Policies).
The University is a participant in the initiative Principles for Responsible Management Education, PRME, supported by the United Nations. The report on the progress in the implementation of the principles for responsible management education is available HERE.
KTU is part of the European University Alliance ECIU University. Sustainability is an integral part of the ECIU University, reflected in all its activities and aiming to create a sustainable future through education, research, and cooperation with industry and society. ECIU University integrates sustainability principles into its learning opportunities to prepare students capable of addressing real contemporary environmental challenges focused on the circular economy, renewable energy, and sustainable infrastructure. In research, ECIU University promotes interdisciplinary approaches to develop innovative and sustainable solutions in the fields of climate change, water resource management, and sustainable construction methods. In collaboration with industry partners and public organizations, ECIU University develops practical solutions that reduce the environmental impact of cities and improve quality of life. ECIU University students are actively involved in sustainability initiatives and community events that foster their engagement and responsibility for building a sustainable future, developing practical skills, critical thinking, and responsible leadership.
This commitment was strongly reinforced during the 2024 ECIU Forum, where sustainability was a key focus across numerous sessions. Students, lecturers, and ECIU staff participated in discussions on topics such as Humanitarian Engineering, Circular Economy, and Digital Twins for Urban Sustainability, demonstrating how ECIU integrates sustainability into both education and research. The forum also highlighted practical applications, like the KTU & Aros Marine collaboration, which focused on circular business models in the marine industry. The session on the “ECIU Green Mobility Guide” emphasized reducing the environmental impact of academic mobility, further illustrating the university’s comprehensive approach to sustainability. The forum’s theme, “Education for a Resilient and Sustainable Society,” captured ECIU’s dedication to making sustainability a fundamental aspect of every lecture, project, and partnership, reinforcing it as a core element of the university’s mission.
Study programmes (#4, #5, #6, #8, #11, #12, #13, #14, #15, #17)
The University provides 4 study programmes that contribute to the Sustainable Development Goals by developing relevant competencies in future members of society:

6.3. By 2030, improve water quality by reducing pollution, eliminating dumping and minimising the release of hazardous chemicals and materials, halving the proportion of untreated wastewater and substantially increasing recycling and safe reuse globally.
Competencies in the preparation of quality drinking water and the prevention of pollution of water bodies are acquired in the modules T270M136 Water Resources Engineering, T490M110 Environmental Biotechnology, T270M137 Waste Management and Resource Recovery Technologies, T270M123 Chemicals in the Environment, P305M010 Methods of Environmental Analysis, T270M121 Modelling of Environmental Processes and Technologies. These issues are also addressed while conducting research in the modules T000M022 Research Project 1, T000M238 Research Project 2 and PR00M123 Final Master’s Degree Project.

7a. By 2030, enhance international cooperation to facilitate access to clean energy research and technology, including renewable energy, energy efficiency and advanced and cleaner fossil-fuel technology, and promote investment in energy infrastructure and clean energy technology.
Competencies in reducing the environmental impact of energy production are acquired in module T270M138 Air Quality Engineering. These issues are also addressed while conducting research in the modules T000M022 Research Project 1, T000M238 Research Project 2 and PR00M123 Final Master’s Degree Project.

9.2. Promote inclusive and sustainable industrialisation and, by 2030, significantly raise the industry’s share of employment and gross domestic product, in line with national circumstances, and double its share in least developed countries.
9.5. Enhance scientific research, upgrade the technological capabilities of industrial sectors in all countries, in particular developing countries, including, by 2030, encouraging innovation and substantially increasing the number of research and development workers per 1 million people and public and private research and development spending.
The study programme focuses on the development of entrepreneurial competencies (T000M239 Eco-Entrepreneurship Project), intensive research development, and the involvement of students in the development of advanced technologies (T270M132 Environmental Nanotechnology), T000M022 Research Project 1, T000M238 Research Project 2, and PR00M123 Final Master’s Degree Project.

11.6. By 2030, reduce the adverse per capita environmental impact of cities, including by paying special attention to municipal and other waste management.
Competencies in the reduction of the negative environmental impact of cities are acquired in the modules T270M138 Air Quality Engineering and T270M137 Waste Management and Resource Recovery Technologies. Students acquire competencies in environmental assessment in the modules T270M123 Chemicals in the Environment, P305M010 Methods of Environmental Analysis, T270M122 Experimental Design and Data Analysis in Environmental Protection and T270M121 Modelling of Environmental Processes and Technologies.

12.5. By 2030, substantially reduce waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling, and reuse.
12.6. Encourage companies, especially large and transnational companies, to adopt sustainable practices and to integrate sustainability information into their reporting cycle.
The principle of resource recovery is a cornerstone of the entire study programme that is applied in all technology modules. Students acquire competencies in waste prevention, recycling and reduction in the module T270M137 Waste Management and Resource Recovery Technologies. Competencies in sustainability and life cycle assessment in products and services are acquired in the module T270M135 Sustainability Management and Law. These issues are also addressed while conducting research in the modules T000M022 Research Project 1, T000M238 Research Project 2 and PR00M123 Final Master’s Degree Project.

13.3. Improve education, awareness-raising and human and institutional capacity on climate change mitigation, adaptation, impact reduction and early warning.
Competencies in climate change prevention, mitigation technologies and adaptation are acquired in the module T270M139 Climate Change Management Technologies.

14.1. Prevent and significantly reduce marine pollution of all kinds, in particular from land-based activities, including marine debris and nutrient pollution by 2025.
Competencies in marine pollution prevention are acquired in the modules T270M136 Water Resources Engineering, T490M110 Environmental Biotechnology, T270M137 Waste Management and Resource Recovery Technologies, T270M123 Chemicals in the Environment, P305M010 Methods of Environmental Analysis and T270M121 Modelling of Environmental Processes and Technologies.

15.5. Take urgent and significant action to reduce the degradation of natural habitats, halt the loss of biodiversity and, by 2020, protect and prevent the extinction of threatened species.
Competencies in ensuring the condition of soil and water bodies as natural habitats are acquired in the modules T490M110 Environmental Biotechnology, T270M136 Water Resources Engineering, T270M123 Chemicals in the Environment, P305M010 Methods of Environmental Analysis and T270M121 Modelling of Environmental Processes and Technologies.

17.16. Enhance the global partnership for sustainable development, complemented by multi-stakeholder partnerships that mobilise and share knowledge, expertise, technology and financial resources, to support the achievement of sustainable development goals in all countries, in particular developing countries.
The study programme is implemented in active cooperation with the social partners. At least 50% of final degree projects analyse the challenges of pollution prevention, reduction, resource recovery and the implementation of sustainability principles in the companies. Research partnerships with scientific and business organisations are developed. At least 50% of final degree projects are developed in the context of research project activities.

6.3 Improving water quality: a) wastewater treatment technologies and systems (T230M177 Sustainable Water Management); b) responsible waste management (increasing recycling and safe reuse and avoiding landfill) (T230M177 Sustainable Water Management, T230M222 Waste Management and Recycling Technologies for Secondary Raw Materials); c) reducing the potential of other pollutants to enter water bodies (T230M177 Sustainable Water Management).
6.4. Improving the water use efficiency: a) equipment and technologies; b) information; c) awareness; d) innovation (T230M177 Sustainable Water Management).

The aim is to provide knowledge about increasing the share of renewable energies and energy efficiency and encourage cooperation between the parties by involving the social partners (lectures, preparation of final degree projects on topics proposed by the social partners, consultation by social partners during the preparation of final degree projects). To encourage students to contribute to clean energy research and technology (T000M265 Research Project 1, T000M266 Research Project 2, T000M164 Final Master’s Degree Project) including renewable energy, energy efficiency, advanced and cleaner fossil fuel technologies and upgrade technologies for sustainable energy services (T230M176 Building Energy Cost Modelling, T230M175 Energy Production and Supply, T230M179 Smart Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning Systems, T230M178 Building Maintenance and Renovation).

The study programme encourages students to contribute to integrating industrial innovation and implementing infrastructure development measures, both during and after their studies.

11.3. By 2030, enhance inclusive and sustainable urbanisation and capacity for participatory, integrated and sustainable human settlement planning and management in all countries (T230M174 Sustainable Buildings and Cities).

Providing students with knowledge about sustainable consumption and production during the entire study programme. Enhancing students’ scientific and technological skills. The faculty’s SDG objective for 2022-2023, the topics of which are encouraged to be included in study modules, topics for final degree projects, etc. The Sustainable and Energy Efficient Buildings study programme is based on this objective.

13.2. Integrate climate change measures into planning (use of renewable energy sources, promotion of renovation, reconstruction, development of modular construction, etc.).

17.16. Enhance the global partnership for sustainable development, complemented by multi-stakeholder partnerships that mobilise and share knowledge, expertise, technology and financial resources, to support the achievement of sustainable development goals and awareness of their importance in society. Students of this study programme listen to lectures on sustainability topics from social partners, teachers share their knowledge with students through international projects and integrate knowledge into their study modules, and the latest technologies and software are used to contribute to the implementation of Sustainable Goals. Cooperation between faculty staff and international social partners working in the field of sustainability. Modules promote sustainable consumption and sustainable decision-making in the construction process.
The University’s mission is to develop future members of society capable of creating high added value. They are unafraid of change, have comprehensive education and can tackle today’s complex problems. They care about the country’s and the world’s challenges and are civic and socially responsible. During their studies, our students learn how to act and live in a multi-ethnic and multicultural environment, and after graduating from the University, they are ready to address the complex challenges of the country and the world. Sustainable development themes are integrated into the study programmes or individual study modules, and societal challenges related to sustainable development and sustainability are addressed in the course of studies.
The following is offered in the study programmes:
For more than two decades, KTU has been organising an exhibition competition for the innovations by young researchers Technorama. Every year, the exhibition presents around 60 innovative solutions in eight areas closely related to sustainable development (areas of solutions are available here). For example, the best solution in 2023 was a game developed by a team of KTU students to promote recycling called Recyclers United.
At the University, semester and final degree projects often focus on Sustainable Development Goals, for example,
The following challenges were addressed in the study module Development of Challenge-Based Innovations (examples):
University teachers and students participate in various studies projects related to sustainable development. Several examples:
PBL South Asia focused on developing competencies and best practices for problem-based learning with a global sustainability theme at South Asian higher education institutions. The project resulted in applied PBL methods being adopted in Nepal and Bhutan and influencing partner institutions. This effort fostered deeper ties between academia and society, improving critical thinking, innovation capacity, and professional skills. It sparked interest in global sustainability-focused PBL and led to spin-off initiatives across Europe, South Asia, and beyond. South Asian institutions seeking to engage with project partners are advised to connect with the PBL South Asia Network coordinated by Indian Institute of Technology Bombay (IITB) and the PBL Lab at Indian Institute of Science (IISc).
Student-led activities encompassed a range of topics, spanning 3 to 18 ECTS credits depending on the course. Examples of these topics included: Affordable housing, Construction waste management, Accessible healthcare, Modular public housing, Modern organic farming, Alleviating traffic congestion in Kathmandu Valley, Solar-powered street lighting systems, Sustainable municipal landfills, Campus natural disaster management plan using CIS, Promoting sustainable tourism, Evaluating the impact of climate change on hydropower generation in Bhutan, Intelligent renewable irrigation systems, Preserving heritage architecture, Innovative construction practices in building operations, and more.
Teachers and mentors from the KTU Faculty of Civil Engineering and Architecture, along with KTU students, travelled to India and Nepal. During these trips, they engaged in collaborative workshops, guided student teams, and contributed to the creation of content for MOOCs and PBL teaching materials.
The University invites all interested students to attend non-formal education courses on sustainable development topics such as “Sustainability in the Construction Sector”, “Upskilling Courses for Experts in the Certification of the Energy Efficiency of Buildings”, “Training Courses for Experts in the Certification of the Energy Efficiency of Buildings”, and “Microbiological Testing Methods for Food and Drinking Water”.
Students and employees are recommended to improve their competencies by studying courses offered on massive open online course platforms, for example, “The Sustainable Development Goals – A global, interdisciplinary vision for the future”, “From Climate Science to Action”, “The Great Sustainability Transition: Global challenges, Local actions”
Every year, the University organises the Earth Day with KTU event, which aims to introduce ecological ideas to students and pupils. Students are encouraged to take an interest in environmental protection, develop critical thinking and notice global problems in terms of future perspectives. https://ktu.edu/events/svesk-zemes-diena-su-ktu/
Students and employees have an opportunity to attend various study modules, including those analysing the aspects of environmental and social sustainability (for example, study modules “Sustainable Human Development”, “Sustainable Development”, etc.). The sustainability knowledge of the participants in the study modules is assessed using a variety of evaluation methods of the learning outcomes.
The University creates an open environment based on the principles of universal design, where the individual differences, potential and contributions of all its employees and students are recognised and valued. The University aims to ensure that all members of the University community have equal opportunities to integrate into the work and study processes, services and activities offered by the University, creating a study, work and research environment in which the community is properly supported, encouraged, accessible, and not subject to discrimination or harassment regardless of the individual or their individual needs. The aim is to make the University’s studies integrated, flexible, high quality and student-centred.
The study process at the University is adapted ensuring equal opportunities for every student. The University financial assistance and support continuously improve the University’s infrastructure to make the University’s physical spaces and information systems accessible to members of the community with visible or invisible disabilities according to the principles of universal design. The study modules included in the study process are taught in buildings, most of which are accessible to people with special mobility needs, e.g., KTU spaces are equipped with lifts, special toilets adapted to people with disabilities, parking lots, tactile surfaces to help people with visual impairments to better navigate through space.
Adaptation of studies is available to students with disabilities or individual learning needs (physical, sensory, complex disorders, mental health problems or other learning disabilities or difficulties): https://students.ktu.edu/studies-accessibility/.
Following the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities and the European Social Charter, the University aims to implement a personalised learning model. Each situation is considered and adapted individually aiming to provide equal opportunities for every community member. The workplace, the presentation of study materials, the concept of assessment, the accessibility of classrooms and the adaptation of teaching/learning spaces for persons with special needs are coordinated by the social welfare coordinator of the Career and Service Centre at the Department of Student Affairs in cooperation with the faculties.
The most vulnerable groups in the University community are provided with an environment for studies, research and work in which hostile, unethical, degrading or offensive actions that violate the honour or dignity of a person or his/her physical or psychological integrity are not tolerated. Students are exposed to a variety of challenges in their daily lives; therefore, their mental health is of great importance to the University. KTU takes full care of students’ physical and psychological well-being by providing free psychological services. It pays great attention to students’ emotional and social well-being of students through self-education and public education lectures, guides, and pastoral after-school activities.
The Department of Student Affairs and the Human Resources Department, in cooperation with the academic community, the Students’ Association and external partners, initiate changes based on student and staff interests and feedback. They provide conditions for community members to disclose information in confidence, without prejudice to personal privacy, avoid discrimination, and provide the right conditions for involvement in the full range of University activities.
The University has ongoing activities to educate the community and foster a culture of equal opportunities by organising various training for administration and faculty on disability awareness, ethics and adaptation of studies, universal design, and equal opportunities.
The University participates in national and international research projects in the field of sustainable development, and develops new technologies to address regional and global environmental challenges; therefore, it is actively involved in international networks of sustainability competencies and is an active member of networks related to sustainable development:

Sustainability is a core principle of ECIU University and is reflected in all its events and initiatives. The 2024 ECIU University Forum was focused not only on academic objectives but also on adopting an environmentally responsible approach to minimize negative environmental impacts. The event aimed to reflect the ECIU University brand, raise awareness, create a sense of community, and inform about European Union funding. Special attention was paid to sustainable solutions when ordering merchandise and organizing the entire event.
Souvenirs to welcome the forum guests: guests were offered high-quality stainless-steel thermos bottles to use instead of single-use cups during the event, along with sturdy, organic cotton reusable bags. Since these products are made of durable materials, they will serve for a long time. Additionally, participants received notepads made from recycled 80 gsm Nautilus Classic paper.
Participant accreditation: accreditation slips and neckerchiefs were made from eco-friendly materials, suggesting that the neck lanyards could be reused for future events.
The main event space: promotional wall and other merchandise was created from materials that can be reused in other activities to reduce waste.
The promotional wall was set up to encourage participants to take photos and share them on social media. The frame is made of aluminium, and the print is on textiles, with the reverse side adapted for general ECIU University information. Both the frame and the textile print will be reused in future events.
Other sustainable merchandise solutions: event materials, speakers’ gifts and other merchandise have been selected according to sustainability principles, using recycled and eco-friendly materials.

Transport: participants were encouraged to use public transport, share rides, and choose environmentally friendly transportation methods. During their travels in Lithuania and Kaunas, participants used trains, public transport, and shared Bolt’s shuttle service.
Food: the food supply was organised to minimise waste, offering a variety of plant-based dishes and ensuring responsible food consumption.
Physical activity: participants were encouraged to walk between different session venues to stay active and maintain their well-being. The Forum sessions were organized in three different KTU buildings: the Santaka Valley, the KTU Library, and the M-Lab Laboratory Centre. Walking from one session location to another took 10-15 minutes.
These solutions underline ECIU University’s commitment to reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainable practices at all events.
The University community is encouraged, empowered and supported by contributing to the coherence of KTU and the region through its personal or departmental activities.
KTU respects human rights and guarantees the rights of its employees.
Coordinating representative – Jurgita Giniūnienė jurgita.giniuniene@ktu.lt

Implementing the principle of gender equality, the University analyzes the gender pay gap and reports to the University Works Council.
The University community is encouraged, empowered and supported by contributing to the coherence of KTU and the region through its personal or departmental activities, in line with the goals of Gender Equality (# 5) and “Decent Work and Economic Growth” (# 8) for World Sustainable Development.
In order to ensure a work-life balance, which is particularly important for the implementation of gender equality, the University provides employees with access to statutory provisions and creates a family-friendly working environment: summer camps are organized for the children of KTU employees; children’s spaces shall be provided where all children of KTU employees can spend meaningful and interesting time during their holidays while their parents are working; prospective first-graders are provided with all the necessary tools and a ‘first-time basket’, not only to help them start a happy school journey, but also to give staff more time to spend on school supplies instead of wasting time shopping for school supplies; Not only employees but also their family members take part in the KTU Employees’ Summer Festival every year. It does not lack good mood and joyful bustle, as a really large group of children gather.
For university staff:
The legal acts adopted by the University regulating the procedures for hiring and evaluating employees, remuneration provisions, the procedure for granting employee leave (including paternity and maternity leave) are based on the universally recognized principles of equality, fairness, internal justice and impartiality and contribute to equal opportunities and diversity. implementation of the policy. Members of the University community are also provided with the opportunity to file appeals on both remuneration and employment relationships in accordance with the procedures set out in the University’s internal legislation.
Since 2022, the university has been running a free emotional health strengthening and education program for employees, provided with the help of external psychologists.
KTU’s infrastructure and administrative activities are an example of achieving the goals of sustainable development.
Coordinating representatives – Gražvydas Visockas grazvydas.visockas@ktu.lt, Agnė Valatkienė agne.valatkiene@ktu.lt

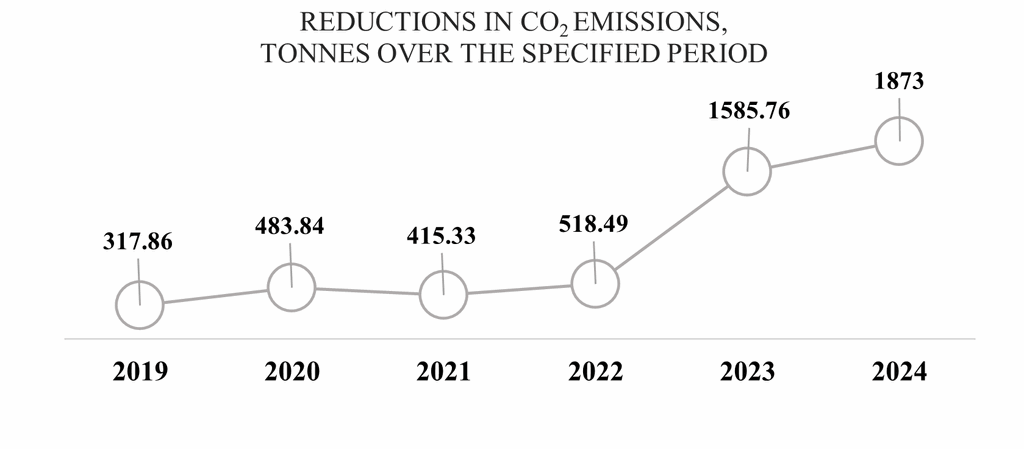
The University’s infrastructure projects aim to contribute as much as possible to the European Union’s green transformation. To this end, it applies energy efficiency solutions in its activities, contributing to the reduction of environmental impact and CO2 emissions. The factors for the implementation of energy efficiency measures are clearly regulated by the legislation of the Republic of Lithuania and the European Union:
KTU chooses renewable energy (# 7; # 9; # 12; # 13)
2019 a hybrid energy production system was developed in the buildings located at Studentu str. 48 and Studentų st. 48 A, which combines technical equipment producing and storing different types of energy, such as a solar power plant (380 kW), a 500 m3 heat storage, a 170 kW heat pump and a waste heat collection system. The data of the system are used in the study programs of the KTU Faculty of Electricity and Electronics. The unique project has won worldwide recognition at the Energy Globe Awards. One and a half thousand innovative ideas from more than 180 countries around the world competed for such recognition.
In 2022, the project “Implementation of renewable energy sources in Kaunas University of Technology buildings”, which started in 2021, was implemented, during which photovoltaic solar power plants were installed in Studentų g. 50, Studentų g. 67, Studentų g. 69, Studentų g. 71, Kaunas. The total capacity of these plants is 464.82 kW. The power plants are expected to generate about 439 310 kWh of electricity per year.
In 2022, solar photovoltaic power plants were purchased from solar parks for KTU buildings at Radvilėnų pl. 19, Studentų str. 56, K. Baršausko g. 59, Kaunas. The total capacity of the purchased solar PV plants is 1199.80 kW.
In 2022, the construction contract works for the twelve-storey dormitory No 10 (Gričiupio g. 13, Kaunas) were completed (complete renovation of the dormitory’s exterior and interior, providing accommodation services that meet the modern needs of students).
In 2023, a 122.85 kW solar photovoltaic power plant is installed on the roof of the KTU building at Studentų g. 54, Kaunas.
In 2023, another remote solar photovoltaic plant with a capacity of 190 kW was installed to supply electricity to the KTU building at 73 K. Donelaičio St., Kaunas.
The modernisation of dormitory No 11 (37 Pašilės Street, Kaunas), which started in 2022, was completed in December 2023. The project achieved energy efficiency class B.
The renovation of the KTU Faculty of Mechanical Engineering and Design was completed in August 2023 to make the building more energy efficient. The project achieved energy efficiency class C.
In the third quarter of 2023, the reconstruction of the building at Studentų g. 63 A was completed. In the reconstructed building is set up the KTU interdisciplinary prototyping laboratory centre “M-Lab”. The project was implemented with the aim of promoting sustainable standards as much as possible: environmentally sustainable construction methods were chosen, existing building structures were used to reduce the consumption of building materials and to make the building as adaptable as possible to the modern needs of the University; polycarbonate panels made of recycled plastic were used for the facade of the building; a modern exterior architecture was implemented to minimise the absorption of the sun’s energy and to allow the building to absorb the heat during the summer. The project was designed to minimise the emission of CO2 greenhouse gases and therefore the building was equipped with a combined heating system: renewable energy sources such as geothermal heat pumps with a variable output of 21 – 88 kW are used for heating. This system is also used for partial cooling of the building: through intermediate heat exchangers, energy is drawn for the operation of the heat pumps, partly from a photovoltaic solar power plant of 37 kW installed on the roof of the building. The building is equipped with the latest Siemens scada desigo building management system, whose main objective is to improve the efficiency of the building’s engineering systems and to fully manage the building’s daily life cycles, while at the same time aiming to reduce the energy resources used for the building’s operation. The solution provides full control of the building’s lighting, the air supply demand through the OHS 1-6 systems, and the heating system, all of which are able to serve only the areas of the building where the activities take place. Variable schedule and sensor-controlled engineering systems allow the building to maximise energy savings and remain an environmentally sustainable building. Thanks to these modern solutions installed in the building, the renovation of the building has achieved an A++ building energy class.
The total reduction in CO2 emissions in tonnes per year as a result of these projects is shown in the figure below.
Sorting waste (# 12)
2019-2020 In the territory of the university instead of the old metal 4-6 cu. m. household waste containers are equipped with 6 underground container blocks with separate tanks for glass, plastic, paper and household waste. Since 2013 sorting boxes for secondary raw materials (paper, plastic, glass, batteries) have been built inside all university buildings (faculties, dormitories, rest rooms). Contracts with waste managers are concluded or renewed annually. Worn out org. the equipment is sold to buyers in accordance with the rules provided by the University. We hand over worn-out old furniture to waste handlers, who deliver it to recycling sites.
Promoting sustainable mobility (# 9; # 11; # 12; # 13; # 3)
In the territory of KTU student campus there are 4 electric charging stations for electric cars, 2 scooter rental points, bicycle storage places are installed next to each building where lectures take place. The dormitories also have storage facilities for scooters and bicycles.
Promoting Responsible and Sustainable Water Consumption (#3, #6, #12)
Kaunas University of Technology has installed a total of 12 drinking water stations, including 9 in academic units, 1 in an administrative building, and 1 in the university’s recreation facility in Palanga.
The installation of water stations is closely linked to the university’s efforts to reduce single-use plastic waste.
You can find drinking water stations in the lobbies of the following buildings: